- Home
- Cable Ladder
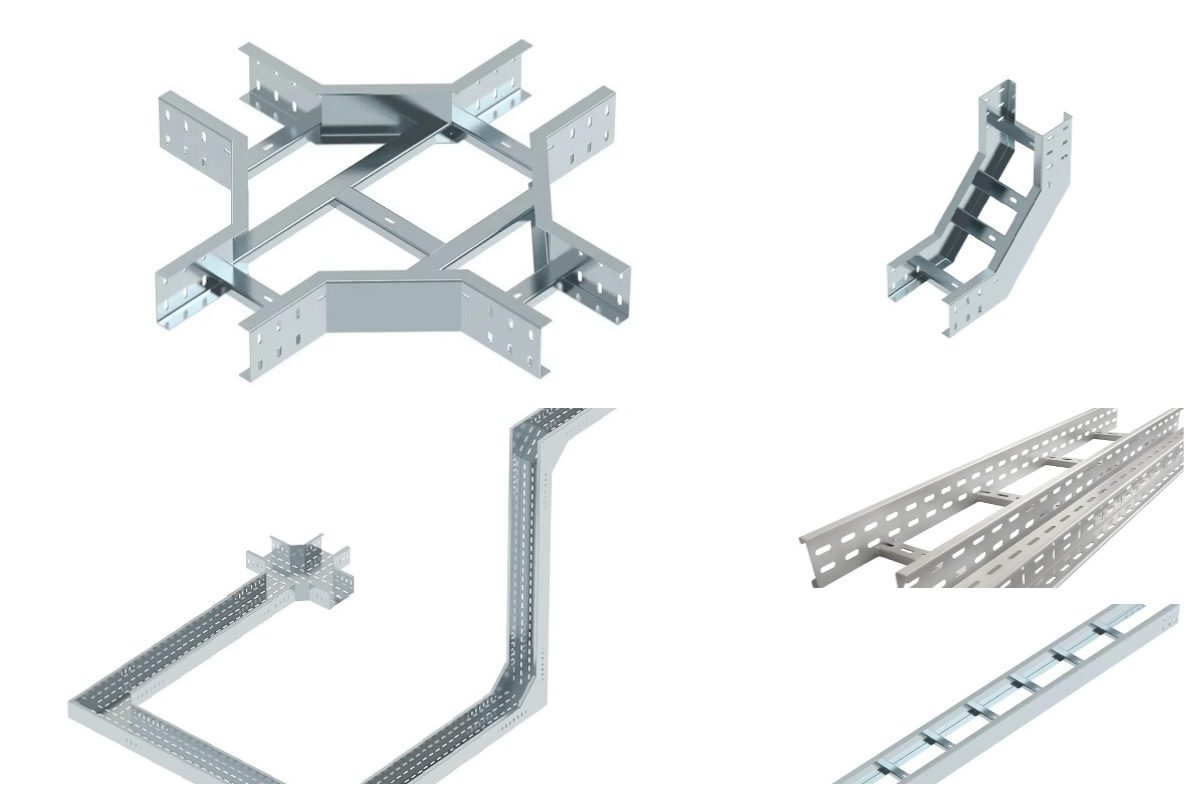
Cable Ladders for Cable Management and Data Center
Cable Ladder of GangLong Fiberglass are made from lightweight and durable tubular steel, designed to support and organize cables in telecommunications and equipment rooms.It also comes with a full range of hardware and accessories for complete installation.They facilitate cable routing along ceilings, walls, and floors, ensuring FRP Cable Ladder are managed efficiently and safely. This organization helps prevent safety hazards and makes troubleshooting and reconfiguring network connections quicker and more effective.
Cable Ladder with horizontal turns for roof-mounted rack routing—fully welded for heavy-duty cable management & organization. Effective cable management is crucial in both residential and industrial settings. Cable Ladders provide a structured pathway for managing large volumes of cables, which prevents tangling, ensures proper airflow, and simplifies maintenance. By protecting cables from harsh conditions and pests, Cable Ladder Racks enhance system safety and efficiency. In commercial buildings and data centers, Cable Ladders are essential for maintaining an organized and reliable network infrastructure. Cable ladder systems are available in versatile sizes, ranging from 12 to 24 inches in width and 10 to 12 feet in length, ideal for routing and facilitating cable runs.
Simplifying Your Life: Key Functionalities
| Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Place of Origin | Hebei, China |
| Brand Name | GangLong Fiberglass |
| Type | Wire Mesh |
| Material | Steel |
| Width | 100mm~900mm Aluminum Cable Ladder |
| Length | Maximum 6000mm Aluminum Cable Ladder |
| Side Rail Height | 50~150mm Aluminum Cable Ladder |
| Maximum Working Load | According to Specifications Aluminum Cable Ladder |
| Finish | Hot-dip Galvanized, Pre-galvanized, Electro-galvanized |
| Material | Stainless Steel, Galvanized Steel, Galvanized Steel |
| Certification | NEMA, CE, UL, S GS, IOS Offshore Cable Ladder |
| Application Environment | Indoor, Outdoor, High Corrosion |
| Minimum Order Quantity | All Quantities are Available in Standard Sizes |
| Shipping Method | Shipping |
News
- Exploring the Benefits of Carbon Fiber Apparel
- How to Work with Carbon Fiber Successfully
- Carbon Fiber Suit: The Future of Lightweight Armor
- Is Carbon Fiber Armor the Future of Protection?
- Why White Carbon Fiber is Popular in Automotive Design
- Transparent Carbon Fiber Sheets Two Sided Gloss Twill
- Epoxy-Compatible Chopped Carbon Fiber Mat
- Carbon Fiber EG Hatch: Upgrade Your Civic Today
- The Benefits of Using Structural Carbon Fibre in Engineering
- How Many Layers of Layered Carbon Fiber Are Needed?
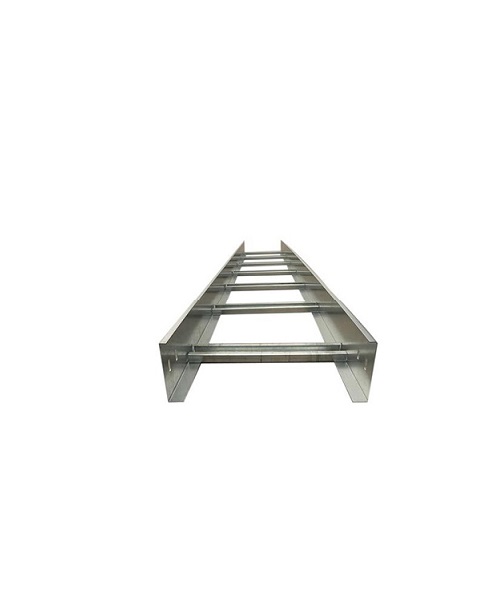

What is a Cable Ladder?
A Cable Ladder is a type of cable management system that provides an open structure for supporting and organizing cables. Typically, it consists of horizontal rungs or rails that are connected by side rails or frames. This open design allows for efficient airflow around the cables, which is essential in preventing heat buildup and ensuring that the cables remain cool and functional. The Cable Ladder is often used in large-scale installations, such as data centers, industrial facilities, and commercial buildings, where managing a large volume of cables is necessary. It provides an easy way to route, maintain, and access cables over long distances, offering both flexibility and durability.
Cable ladders are designed to be versatile, accommodating a wide variety of cable types, including power cables, fiber optics, and low-voltage cables. Their open nature allows for convenient expansion and reconfiguration, making them ideal for installations where modifications or additions are likely to occur.
Advantages of Using a Cable Ladder
A Cable Ladder provides several distinct advantages over other cable management systems, particularly in environments where efficiency, accessibility, and durability are crucial. Here are the main reasons to choose a cable ladder over alternative products:
Superior Airflow and Cooling
The open design of a cable ladder allows for excellent ventilation around the cables. Proper airflow helps to prevent overheating, which is critical for ensuring that cables, especially high-voltage or high-performance ones, operate efficiently and maintain their longevity. Other systems, such as enclosed cable trays, may restrict airflow, leading to higher temperatures and potential performance issues.
Ease of Access for Maintenance
One of the key benefits of a cable ladder is its accessibility. The open structure makes it easy to reach cables for maintenance, troubleshooting, or upgrades. This is particularly valuable in environments where cables are subject to frequent changes or need regular inspection. Accessing cables in a traditional cable tray can be more difficult, as they are enclosed, which can complicate repairs or modifications.
Heavy Load Capacity
Cable ladders are ideal for supporting heavy cables over long distances. Their robust design allows them to bear significant cable loads without sagging, which is essential in large-scale industrial or commercial installations. They are especially suitable for high-voltage power cables and other heavy-duty cables that require strong support.
Cost-Effective for Long Spans
Due to their strength and load-bearing capacity, cable ladders can span longer distances without needing additional support brackets. This makes them a cost-effective solution for large projects where multiple support points would increase installation costs. Cable trays, in contrast, may require more frequent support brackets, adding to the overall cost.
Easy to Expand or Modify
The open design of the cable ladder allows for quick and easy modifications. If additional cables need to be added to the system, it can be done without significant disruption. In environments where installations are subject to constant changes, cable ladders provide the flexibility required for growth and expansion.
Applications of Cable Ladders
Cable ladders are widely used in a variety of industries and settings, where large volumes of cables need to be managed and protected. Their versatility and adaptability make them an ideal choice for the following applications:
Data Centers
In data centers, where high-density cable management is essential, cable ladders are ideal due to their ability to support heavy cable loads while maintaining excellent airflow around the cables. The open structure helps dissipate the heat generated by the numerous cables, preventing overheating and ensuring the smooth functioning of sensitive equipment. Additionally, the easy accessibility of cables in a ladder system allows for quick maintenance, troubleshooting, and upgrades as the network evolves.
Industrial Installations
Industrial environments often involve harsh conditions, such as exposure to dust, moisture, and chemicals. Cable ladders are beneficial here because they provide a sturdy and reliable means of organizing cables while allowing them to breathe. However, in some cases, additional protective covers or shields can be added to the open rungs to protect cables from external factors. Cable ladders also allow for the safe routing of cables across large factory floors or equipment areas, making them a versatile solution in industrial settings.
Commercial Buildings
In commercial buildings, especially in spaces like offices, retail stores, or shopping malls, cable ladders are an excellent solution for managing network, power, and communication cables. They provide an efficient way to route cables across the building’s infrastructure, whether overhead or along walls. The open structure allows for easy modifications or expansions of the cable system as new technologies or systems are added. Additionally, their ability to handle large cable volumes ensures that cable management remains neat and organized, even in complex installations.
Telecommunication Networks
Telecommunications companies often use cable ladders to organize the vast number of cables required for their networks. In telephone exchange buildings, data transmission facilities, or towers, cable ladders provide a durable and accessible means of supporting both power and data cables. Their design is particularly useful for long cable runs that need to be supported over large spans.
Large-Scale Commercial Installations
Large commercial installations such as airports, sports arenas, and stadiums require extensive cable management solutions to handle complex electrical and communication systems. Cable ladders provide the flexibility to manage large numbers of cables while keeping them safe and organized. These systems can be expanded or reconfigured as the installation grows or undergoes updates, ensuring that the infrastructure supports the increasing number of cables needed.
Pulp & Paper and Manufacturing Plants
In manufacturing plants like pulp and paper mills or factories with complex machinery, cable ladders can be used to support cables that are routed through harsh, high-temperature environments. The ladders’ durability allows them to support large bundles of cables over long distances, while the open structure ensures that cables are not subjected to heat buildup or damage, which could impact the manufacturing process.
Cable ladders are an effective and versatile solution for managing cables in a wide range of environments. Their open design offers numerous advantages, including superior airflow, easy access for maintenance, and the ability to support heavy cable loads over long distances. They are particularly useful in data centers, industrial settings, commercial buildings, and other large-scale installations. With their flexibility, durability, and cost-efficiency, cable ladders remain one of the most reliable cable management options available.
Cable Ladder vs. Cable Tray: A Comparison Overview
When choosing between a cable ladder and a cable tray, it’s essential to understand their distinct designs, functionalities, and suitability for various environments. Both are commonly used for cable management in industrial, commercial, and residential installations, but each has unique advantages depending on the project’s requirements. Additionally, FRP cable tray offer a corrosion-resistant alternative suitable for harsh or outdoor environments where traditional metal trays may not perform as well.
| Aspect | Cable Ladder | Cable Tray |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Open structure with horizontal rungs and side rails creating an open pathway for cables | Enclosed or perforated base with side rails forming a protective channel for cables |
| Airflow | Excellent airflow reduces heat buildup | Limited airflow, especially with solid bases, may cause heat accumulation |
| Cable Access | Easy to access cables for maintenance, repairs, and upgrades | More difficult access due to enclosed or semi-enclosed design |
| Load Capacity | Suitable for heavy cable loads and long spans without frequent supports | Generally supports lighter to moderate cable loads; heavy loads may require extra supports |
| Protection | Cables are exposed to dust, moisture, and physical damage | Provides better protection against dust, moisture, and physical impact |
| Aesthetics | Less visually appealing because cables are exposed | Offers cleaner and more organized appearance |
| Typical Applications | Large industrial sites, power plants, heavy-duty installations | Commercial buildings, data centers, retail environments |
| Advantages | Superior ventilation, easy cable access, ideal for heavy loads and long cable runs | Enhanced cable protection, cleaner appearance, better cable containment |
| Disadvantages | Cables exposed to environment, vulnerable to damage, less aesthetic | Restricted airflow, harder cable access, less suited for heavy cables without additional support |
| Best Use | Environments needing heavy cable support, good ventilation, and easy maintenance | Environments prioritizing cable protection, aesthetics, and organized appearance |

Thank you for your interest in our products. To receive our pricelist or for any inquiries, please fill out the form below. We will get back to you within 24 hours.

Cable Ladder Sizes
Standard Sizes of Cable Ladders
Cable ladders come in a range of standard sizes to accommodate different installation requirements. These sizes vary primarily in terms of width and length, offering flexibility for various cable loads and spatial constraints. The most common dimensions for cable ladders are:
Widths: Ranging from 12 inches to 24 inches. The width you choose depends on the number and size of cables you need to manage. A narrower ladder (e.g., 12 inches) is suitable for smaller or fewer cables, while a wider ladder (e.g., 24 inches) can handle larger cable bundles or cables with more space between them to ensure easy routing and airflow.
Lengths: Typically available in lengths of 10 feet to 12 feet. Standard lengths are convenient for most installations, and multiple sections can be easily connected to create longer cable runs as needed. The length of the ladder should be chosen based on the span between supports and the distance over which cables need to be routed.
For most installations, the typical standard sizes include:
- 12″ Width x 10′ Length: Suitable for smaller, lighter cable loads.
- 18″ Width x 10′ Length: A middle ground option, accommodating moderate cable loads and offering more space for airflow.
- 24″ Width x 10′ Length: Best for heavy-duty applications with large cable bundles that require additional space for safe routing and ventilation.
Advantages and Usage Ranges of Different Sizes
Narrower Cable Ladders (12″ to 18″ wide): These are ideal for smaller cable loads or where space is limited. They work well in environments where only a small number of cables need to be routed, such as smaller data centers or low-capacity commercial spaces.
Wider Cable Ladders (18″ to 24″ wide): Wider ladders are suited for more significant cable runs, including power cables or high-density installations. The extra width allows for better cable organization, improved airflow, and easier maintenance. These sizes are commonly used in industrial settings, large-scale commercial buildings, or data centers with extensive cable management needs.
Longer Cable Ladders (10′ to 12′ length): Longer ladders are necessary for large installations where cables need to be routed over longer distances. They reduce the need for additional joints or connectors, offering a more seamless solution for lengthy cable runs.
Choosing the Right Cable Ladder Size
Selecting the right Cable Ladder size is crucial for ensuring a safe and effective cable management system. The process of choosing the appropriate size involves several key considerations:
Determine the Cable Load
The most important factor in selecting the right ladder size is the load of cables it needs to support. Heavy cables or high-density bundles may require a wider ladder (18″ or 24″) for optimal stability and organization. For lighter loads or fewer cables, a 12″ width might suffice.
Consider the Installation Environment
The environment where the cable ladder will be installed also plays a role in determining size. For environments with high temperatures or hazardous conditions, larger ladders may offer better air circulation, reducing the risk of overheating. If the installation site has obstructions (e.g., ceilings, walls), ensure that the ladder width and length can navigate these restrictions without causing issues during installation or use.
Evaluate the Required Span and Support
The span between supports is another key factor in sizing the ladder. Larger spans may require more robust and wider ladders to prevent sagging or deflection. For shorter spans, a narrower ladder may be sufficient. The ladder length should align with the installation’s layout, ensuring it can cover the required distance without too many joints or support points.
Account for Future Modifications
Think about future needs. If your installation may require additional cables in the future, it’s better to choose a slightly larger ladder (such as a 18″ or 24″ width) to allow room for expansion without needing a complete redesign of your system.
Select the Appropriate Material and Strength
Ensure that the material of the ladder (steel, aluminum, FRP, etc.) and its strength rating match the load and environmental factors. Heavier cables and more demanding environments may require sturdier materials, which can also influence the ladder’s size.
By understanding the standard sizes of cable ladders and the factors influencing the right size for your installation, you can ensure optimal cable management. Whether you’re dealing with small commercial setups or large-scale industrial installations, selecting the appropriate width, length, and material will ensure that your cables are supported, accessible, and well-protected throughout their lifespan.
Heavy Duty Cable Ladder
What is a Heavy Duty Cable Ladder?
A Heavy Duty Cable Ladder is a specialized cable management system designed to handle higher load capacities and to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Unlike standard cable ladders, which are suitable for lighter or medium-duty applications, heavy duty cable ladders are constructed with reinforced materials and enhanced support structures to bear heavy cable bundles without compromising stability or safety. These ladders are typically used in environments where large quantities of power cables, networking cables, or other industrial-grade wiring need to be managed efficiently and securely.
Heavy Duty Cable Ladders are commonly made from high-strength materials such as galvanized steel or stainless steel, providing resistance to corrosion, extreme temperatures, and physical wear. They offer the durability needed for demanding installations in industrial, commercial, and infrastructure projects.
Difference Between Heavy Duty Cable Ladders and Other Cable Ladders
The key differences between Heavy Duty Cable Ladders and standard cable ladders lie in their material strength, construction design, and load capacity:
Load Capacity: Heavy Duty Cable Ladders are specifically designed to support larger, heavier cable bundles. Standard cable ladders may handle lighter loads, making them unsuitable for high-demand applications.
Material Construction: Heavy duty models are typically made from stronger, corrosion-resistant materials such as galvanized steel or stainless steel, whereas standard cable ladders may use lighter materials like aluminum, which may not provide the same level of durability under heavy load or extreme conditions.
Design Reinforcements: Heavy Duty Cable Ladders feature reinforced side rails, additional rungs, and a more robust frame structure. This allows them to carry heavier loads over longer spans without sagging, unlike standard ladders which may require additional support for similar applications.
Applications: While standard cable ladders are suitable for lighter-duty installations such as in commercial buildings or residential projects, heavy-duty cable ladders are essential in industrial environments, data centers, and other areas where cables are subjected to higher physical stresses, heat, or extreme weather conditions.
Features of Heavy Duty Cable Ladders
Heavy Duty Cable Ladders are engineered to meet the needs of demanding cable management systems. Key features include:
Reinforced Construction
These ladders are built with reinforced side rails and extra rungs, providing additional strength to support heavy cable bundles and reduce the risk of deflection or damage.
Corrosion Resistance
Made from materials like galvanized steel or stainless steel, heavy-duty cable ladders resist rust and corrosion, ensuring long-lasting performance even in harsh environments, such as outdoor or chemical plants.
High Load Capacity
Designed to carry large bundles of cables, heavy-duty cable ladders can support up to several hundred pounds per section, depending on the material and configuration. This makes them ideal for large-scale industrial setups and power plants.
Advanced Mounting and Support
Heavy duty ladders come equipped with advanced mounting systems and additional support brackets. These ensure that the ladder maintains its stability under heavy loads, especially over long spans.
Temperature Resistance
Built to endure high temperatures, these ladders are suitable for environments like power plants, manufacturing facilities, and data centers, where cables need to be routed through areas with significant heat or exposure to outdoor elements.
Easy Maintenance
The open structure of a cable ladder allows for easy access to cables for maintenance, installation, or future modifications, reducing downtime during operational adjustments.
Applications of Heavy Duty Cable Ladders
Heavy Duty Cable Ladders are used in a variety of industrial, commercial, and infrastructural applications that demand high strength, durability, and reliability. Key areas of use include:
Industrial Settings
In industries like oil & gas, chemical plants, and manufacturing facilities, heavy-duty cable ladders are used to support large, high-voltage power cables, control wiring, and communication cables. They are built to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, dust, and chemical exposure.
Power Plants
Heavy-duty ladders are essential in power generation plants for routing large quantities of electrical cables across long distances. These systems require high load-bearing capacity to manage the extensive cabling needed for electrical infrastructure, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Data Centers
In data centers, where cable management is critical to both functionality and safety, heavy-duty cable ladders provide a secure pathway for large bundles of networking cables. These ladders help to maintain airflow and prevent overheating, which is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in high-density installations.
Infrastructure Projects
Heavy-duty cable ladders are also employed in the construction of infrastructure projects such as highways, tunnels, and airports. They manage the cables used for electrical systems, communication, and security, while offering protection against environmental hazards.
Telecommunication
Heavy-duty ladders are used to manage extensive wiring for telecommunication networks, supporting large numbers of fiber optics and power cables in facilities like telecom towers, switching stations, and network hubs.
Transportation and Airports
In airports and railways, heavy-duty cable ladders are used to route cables that power lighting, communication systems, and other critical infrastructure, ensuring these systems remain organized and functional under heavy use.
Heavy Duty Cable Ladders provide the necessary strength and durability for cable management systems in demanding environments. Their reinforced construction, corrosion resistance, and high load-bearing capacity make them ideal for industrial, commercial, and infrastructural applications. Whether used in data centers, power plants, or manufacturing facilities, these cable ladders ensure efficient cable routing, maintain cable integrity, and provide easy access for ongoing maintenance, making them an indispensable choice for large-scale installations.
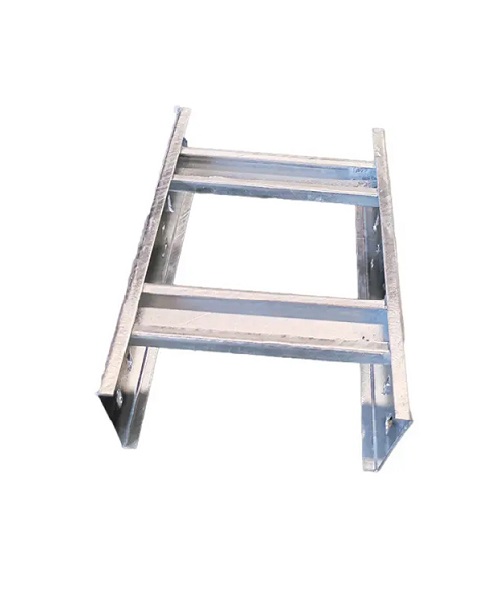
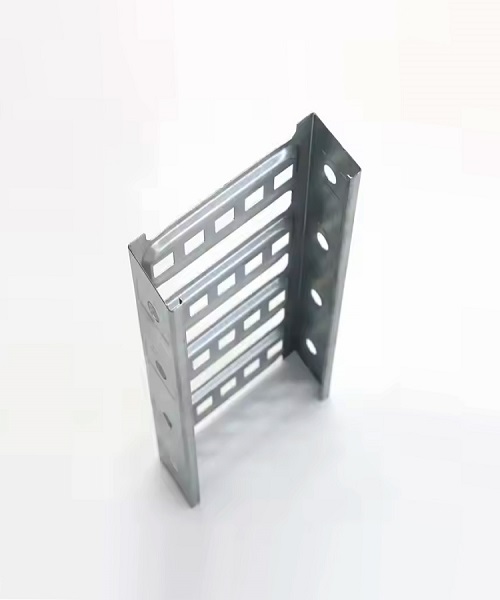


Cable Ladder Runway
What is a Cable Ladder Runway?
A Cable Ladder Runway is a type of cable management system designed to provide a continuous, sturdy pathway for cables over long distances. It consists of a series of parallel ladder sections that are connected to form a seamless route, allowing cables to be easily routed and organized across large areas. This system is particularly beneficial in environments where extensive cable runs are necessary, such as in data centers, telecommunications facilities, and large industrial plants.
Cable Ladder Runways are ideal for installations that require minimal support points, making them efficient for managing large volumes of cables without unnecessary complexity. The runway configuration is designed to support a wide variety of cable types, ensuring optimal spacing and airflow, which is critical for maintaining cable performance and reducing the risk of overheating or damage.
One of the primary benefits of a Cable Ladder Runway is the continuous design, which eliminates the need for multiple support structures. This creates an uninterrupted path for cables, reducing clutter and making the system easier to manage. The runway system helps keep cables neatly organized and properly spaced, preventing tangling or interference. This not only improves the appearance of the installation but also makes it easier to maintain and upgrade cables in the future. With its open design, a Cable Ladder Runway promotes airflow around the cables, which helps to dissipate heat and prevent cables from overheating. Proper airflow is crucial, especially in high-density installations like data centers or industrial plants. These systems are designed to support large numbers of cables, including heavy power cables, fiber optics, and other critical wiring, making them ideal for environments with substantial cable runs. Made from high-strength materials like galvanized steel or aluminum, Cable Ladder Runways are built to withstand the rigors of demanding environments, including extreme temperatures, moisture, and physical stresses. By reducing the need for additional cable management components like supports or junction boxes, a Cable Ladder Runway can be a more cost-effective solution for large-scale installations. Installing a Cable Ladder Runway is relatively straightforward and can help streamline the cable management process. Key installation considerations include: Planning the Layout: Before installation, it’s important to plan the layout of the cable ladder runway. This includes determining the optimal path for the ladder, the required number of ladder sections, and the locations of support points. Planning ahead ensures that the system is both functional and efficient. Minimal Support Points: One of the main advantages of the Cable Ladder Runway is that it requires fewer support points than other types of cable management systems. However, adequate support must still be provided at strategic intervals to ensure the ladder remains stable and level over long distances. Connecting Ladder Sections: The individual ladder sections are typically connected using brackets or bolts, forming a continuous path for the cables. This process is relatively quick, and the sections are designed to fit securely together to create a stable, long-lasting system. Cable Routing: Once the ladder runway is installed, cables can be routed along the ladder. Cables should be placed in a manner that maximizes airflow and avoids excessive strain or tight bends. Cable ties or clips can be used to keep cables organized and secure along the length of the ladder. Flexibility for Future Modifications: The Cable Ladder Runway offers flexibility for future changes or additions. Cables can be easily added or removed, and the design allows for easy modifications as the installation grows or changes over time. The Cable Ladder Runway is an efficient, robust, and flexible solution for large-scale cable installations. Its continuous design and ability to support heavy loads make it ideal for demanding environments like data centers, industrial facilities, and telecommunications installations. The benefits of a cable ladder runway, including improved airflow, efficient cable management, and easy installation, make it a go-to option for large cable runs. Proper planning and installation ensure a streamlined and organized system that will serve the needs of your facility for years to come.Benefits of a Cable Ladder Runway
Continuous Cable Pathway
Efficient Cable Management
Improved Airflow and Cooling
Support for Heavy Loads
Durability
Cost-Effective
Installation of a Cable Ladder Runway
Cable Ladder Rack Accessories
Essential Accessories
Cable Ladder Rack Accessories are crucial components that enhance the functionality and integration of Cable Ladders within various installations. These accessories include:
Brackets: Designed to secure the cable ladder to walls, ceilings, or other structures, brackets provide essential support and stability. They come in various styles, such as wall brackets, ceiling brackets, and adjustable brackets, to accommodate different installation needs.
Supports: These include vertical supports, standoff supports, and additional support channels that help maintain the proper alignment and spacing of the Cable Ladder. Supports are vital for ensuring that the ladder remains level and can bear the weight of the cables it carries.
Junctions: Junctions such as T-junctions, corner brackets, and splicing kits allow for flexible routing of cables by connecting multiple segments of the ladder. These accessories enable seamless transitions and changes in direction, ensuring a continuous pathway for cables.
Cable ladder rack accessories provide essential support and secure mounting points that significantly improve the stability of cable ladder systems. By preventing sagging, shifting, or misalignment, these accessories ensure the ladder maintains its structural integrity under heavy cable loads and long spans. This enhanced stability reduces the risk of mechanical failure and prolongs the system’s lifespan, contributing to safer and more reliable cable management in industrial and commercial installations. Adjustable brackets, clamps, connectors, and hangers simplify the installation process by allowing easy adjustments to fit complex building layouts. These accessories enable installers to customize cable ladder configurations to meet unique project requirements quickly. The flexibility they offer reduces installation time and labor costs, making setup more efficient. Furthermore, their adaptability ensures that cable ladders can accommodate future expansions or modifications without extensive rework. Accessories such as cable ties, dividers, and separators help maintain neat and orderly cable arrangements within the ladder system. Proper cable separation prevents tangling, reduces the risk of damage, and minimizes electromagnetic interference. Organized cable runs improve airflow around cables, promoting better heat dissipation. Overall, enhanced organization leads to a cleaner, safer installation that is easier to manage and visually appealing. Using the right accessories facilitates easier access to individual cables, streamlining maintenance and troubleshooting tasks. Technicians can quickly identify and isolate faults or perform repairs without disrupting the entire system. This accessibility reduces downtime and improves operational efficiency. Well-supported and organized cable ladders make routine inspections faster and less error-prone, ensuring that the cable infrastructure remains reliable and safe over time.Benefits of Cable Ladder Rack Accessories
Enhanced Stability and Support
Simplified Installation and Flexibility
Improved Cable Organization
Easier Maintenance and Troubleshooting
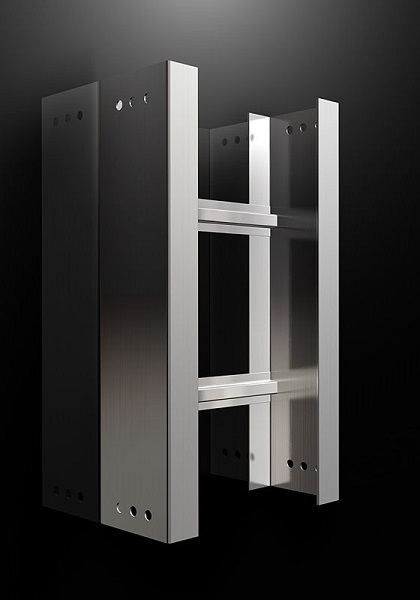

Ganglong Fiberglass Supply Various Size Cable Ladder
Efficient Cable Management with Ganglong Fiberglass Cable Ladders
Ganglong Fiberglass cable ladders are widely used in wiring systems, ensuring a smooth and organized cable layout. Designed to support large, heavy cables between two points, these cable ladders are particularly suitable for high- and low-voltage power cables. Compared to isolated cable tray, cable ladders offer excellent airflow and heat dissipation while providing greater stability and load capacity than wire mesh trays.
Material Options for Cable Ladders
Selecting the right material for cable ladders depends on the installation environment and conditions. Ganglong Fiberglass provides a variety of materials to suit different applications:
- Pre-Galvanized Carbon Steel – Compliant with AS1397, ideal for indoor applications.
- Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel – Meets BS EN ISO 1461 standards, suitable for outdoor use.
- Stainless Steel (SS304/SS316) – The most durable and robust material, offering maximum corrosion resistance.
- Powder-Coated Carbon Steel – Manufactured to JG/T 3045 standards for added protection.
- Aluminum – Lightweight, durable, and compliant with AS/NZS 1866 standards.
- Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) – Built to AS 30135 standards for high resistance to corrosion and chemicals.
- Electropolished Stainless Steel – Conforms to ISO 4995, offering superior corrosion resistance and a polished finish.
To enhance adaptability and ensure smooth cable routing, Ganglong Fiberglass offers a range of accessories, including: Ganglong Fiberglass supplies cable ladders in various sizes to meet diverse industrial and commercial needs. These ladder trays are installed as a system, connecting straight sections, fittings, and accessories to form a continuous cable routing channel. The lightweight aluminum construction ensures ease of handling and corrosion resistance, making it an optimal choice for modern installations. With a commitment to responsible business operations and sustainable energy solutions, Ganglong Fiberglass supports efficient power management. By leveraging electrification and digitalization, our company helps industries transition to renewable energy and addresses global power challenges effectively. Ganglong Fiberglass remains a trusted partner for cable management solutions, providing high-quality, customizable cable ladders that meet the demands of modern infrastructure projects.Essential Accessories for Cable Ladders
Customization and System Integration
Commitment to Sustainability and Power Management
FAQs about Cable Ladder
What is the size of a standard cable ladder?
What is a ladder of cords?
What is a cable ladder used for?
How much weight can a cable tray hold?
Can you stack cables in a cable tray?
Which type of ladder should you not use when you work with exposed wires?
What is the difference between a cable tray and a trunking?
Trunking: Trunking, or cable trunking, is a closed, often rectangular, conduit used to enclose and protect cables. It is typically used in environments where cables need to be hidden for aesthetic reasons or to protect them from physical damage. Trunking provides a more contained route for cables compared to open cable trays.
When to use a cable basket?
Data Centers: To manage high volumes of data cables and maintain airflow.
Commercial Buildings: For routing low-voltage and power cables.
Maintenance and Upgrades: Because it allows easy access to cables for modifications or troubleshooting.
Why do electricians use fiberglass ladders?
Which ladder is safe for electrical work?
Where do you use a ladder type cable tray?
Industrial Settings: For routing and managing power and control cables.
Commercial Buildings: In areas where high cable densities are required.
Data Centers: To organize and support network and data cables while ensuring good airflow.
What is another name for a cable tray?
How do you size a cable ladder?
Determine Cable Quantity: Calculate the total number of cables and their sizes that will be routed through the ladder.
Assess Cable Dimensions: Measure the diameter or width of the cables to ensure they fit within the ladder’s dimensions.
Consider Load Requirements: Ensure the ladder can support the weight of the cables, including any future expansions. Check the load rating provided by the manufacturer.
Select Ladder Width and Depth: Choose a ladder width that allows for the required cable volume while maintaining space for proper ventilation. The depth should be adequate to support the cables and provide stability.
Check for Regulatory Compliance: Verify that the selected ladder size meets local codes and industry standards for cable management.
How do you calculate cable sizing?
Determine Electrical Load: Identify the total current (in amps) that the cable will carry.
Consider Voltage Drop: Calculate the acceptable voltage drop over the cable length. Higher loads or longer distances may require larger cables to minimize voltage drop.
Select Cable Material and Insulation: Choose the appropriate material (e.g., copper or aluminum) and insulation type based on environmental conditions and electrical requirements.
Use Standard Calculations or Software: Utilize cable sizing charts, tables, or software tools that consider current-carrying capacity, voltage drop, and environmental factors to determine the appropriate cable size.
How do you measure the size of a ladder?
Width: Measure the distance between the side rails of the ladder. This is important for determining how many cables the ladder can accommodate.
Depth: Measure the distance from the back to the front of the ladder, which affects cable management and support.
Length: Measure the length of the ladder from end to end, which determines how far the ladder will extend in the installation.
What is the standard length of ladder cable tray?
How often do you have to support a cable tray?
General Guidelines: For standard cable trays, supports are usually placed every 4 to 6 feet (1.2 to 1.8 meters).
Heavy-Duty or Larger Trays: Supports may be required more frequently, every 5 feet (1.5 meters) or less, depending on the load and span.
What is the minimum distance between cable trays?
How far apart are cable tray support spaces?
For Standard Trays: Supports are spaced every 4 to 6 feet (1.2 to 1.8 meters).
For Heavy-Duty Trays: Supports may be spaced closer, every 5 feet (1.5 meters), depending on the load and configuration.
How do you calculate cable trunk size?
Determine Cable Volume: Assess the number and size of cables that will be routed through the trunk.
Account for Cable Spacing: Allow for adequate spacing between cables to avoid overheating and facilitate maintenance.
Choose Trunk Dimensions: Based on the total cable volume and spacing requirements, select a trunk size that accommodates the cables while meeting safety and regulatory standards.
How do you calculate cable tray fill?
Calculate Tray Area: Determine the internal dimensions of the cable tray.
Measure Cable Dimensions: Measure the diameter or width of the cables.
Compute Fill Ratio: Use the formula:
Fill Ratio=Total Cable Volume ÷ Tray Volume. Ensure the fill ratio does not exceed recommended limits, typically 50% to 70% of the tray's cross-sectional area, depending on regulations and manufacturer guidelines.
How thick is heavy duty cable ladder?
Steel Ladders: Typically have a thickness ranging from 0.06 to 0.125 inches (1.5 to 3.2 millimeters).
Aluminum Ladders: Generally have a thickness of around 0.08 to 0.125 inches (2 to 3.2 millimeters).
Where would you use a cable ladder?
Industrial Facilities: To manage power and control cables.
Data Centers: For organizing and cooling network and data cables.
Commercial Buildings: In areas requiring substantial cable management and support.
Power Plants: To handle high-voltage cables and ensure proper ventilation.
What is the best type of ladder to use around electrical equipment?
What is the difference between a raceway and a cable tray?
Cable Tray: A cable tray is an open framework used to support and organize cables. It allows for easy access, ventilation, and is typically used in environments where large volumes of cables are present. Cable trays come in various styles, including ladder trays, perforated trays, and solid-bottom trays.
How do you use a portable ladder safely?
Inspect the Ladder: Check for any damage or defects before use.
Position Correctly: Place the ladder on a stable, level surface and ensure it is properly angled (approximately 75 degrees).
Secure the Ladder: If possible, secure the ladder at the top to prevent movement.
Maintain Three Points of Contact: Always keep two hands and one foot, or two feet and one hand in contact with the ladder.
Avoid Overreaching: Move the ladder as needed to avoid overreaching, which can destabilize the ladder.
Where are perforated cable trays most frequently found?
Commercial Buildings: For organizing and managing electrical and data cables.
Industrial Settings: Where ventilation and cable accessibility are important.
Data Centers: To support and route network cables while allowing airflow.
Which ladder would you use to work near electric wires?
What is the purpose of a cable tray?
What is the difference between cable basket and cable tray?
Cable Tray: A cable tray is a broader term that includes various types of trays used for cable management. It includes ladder trays, perforated trays, and solid-bottom trays, and can support a wider range of cable loads and configurations.
Which cords or cables can be run in a ladder tray in a damp location?
Waterproof Cables: Designed specifically for use in wet or damp environments.
Corrosion-Resistant Cables: With coatings that resist moisture and corrosion.
Indoor/Outdoor Rated Cables: Suitable for environments where exposure to moisture is possible.
What are the advantages of ladder cable tray?
Ventilation: The open design allows for excellent airflow, reducing the risk of overheating.
Accessibility: Easy to install, modify, and access cables for maintenance.
Flexibility: Suitable for large volumes of cables and allows for expansion.
Strength: Provides robust support for heavy cable loads and equipment.
Where is ladder type cable tray used?
Industrial Facilities: To support large volumes of power and control cables.
Data Centers: For managing network and data cables.
Commercial Buildings: Where high-density cable management is required.
Power Plants: For routing and supporting high-voltage cables.
Where do you run cables in walls?
Conduits or Raceways: Protect cables from damage and provide a clear path.
Cable Trays or J-Hooks: Secure cables in place and prevent sagging.
Drilled Holes: For routing cables through studs and partitions, ensuring compliance with building codes and maintaining proper separation from other systems.
What is the difference between cable duct and cable tray?
Cable Tray: A cable tray is an open framework that supports and organizes cables. It allows for ventilation and easy access, making it suitable for environments with large volumes of cables and where accessibility is crucial.
What are the three main types of cable trays?
Ladder Tray: Consists of two side rails connected by rungs, resembling a ladder. It provides strong support for heavy cables and allows for excellent ventilation and easy access.
Perforated Tray: Features a solid base with perforations that allow for cable ventilation and easy mounting of cable ties. It is suitable for general cable management and provides good support and accessibility.
Solid-Bottom Tray: Has a continuous, solid base which provides protection against dust and debris. It is used in environments where additional protection is needed for the cables.
What is the spacing for ladder cable tray rungs?
Which cable tray is best?
Ladder Tray: Best for heavy-duty applications where ventilation and accessibility are crucial.
Perforated Tray: Suitable for general cable management where moderate ventilation and support are required.
Solid-Bottom Tray: Ideal for environments where additional protection from contaminants is necessary.
What is the best tool for cutting cable trays?
Metal Cable Trays: Use a metal cutting saw or a pipe cutter. For precise cuts, a band saw or circular saw with a metal-cutting blade can also be used.
Fiberglass Cable Trays: Use a saw designed for cutting fiberglass, such as a jigsaw with a fine-toothed blade.
What is the difference between cable tray and channel tray?
Channel Tray: A type of cable tray that is narrower and usually has a U-shaped or channel profile. It is used for smaller quantities of cables and provides a more compact, enclosed path compared to standard cable trays.
What is the difference between cable tray and raceway?
Raceway: An enclosed conduit system used to protect and route cables. It can be made from metal or plastic and provides a more discreet path for cables, often used for aesthetic reasons or to protect cables from physical damage.
What are the five basic cable trays fittings?
Elbows: Used to change the direction of the cable tray run.
Tees: Allow for a branch-off from the main cable tray route.
Reducers: Used to change the size of the cable tray from a larger to a smaller section.
Supports: Provide support and stability for the cable tray system.
Covers: Enclose the cable tray to protect cables and provide a cleaner appearance.
What is the difference between cable trunking and cable tray?
Cable Tray: An open framework that supports and organizes cables, allowing for easy access and ventilation. It is used for managing large volumes of cables in industrial and commercial settings.
What is the difference between a cable ladder and a cable tray?
Cable Tray: A broader term that includes various styles of trays (such as ladder, perforated, and solid-bottom) used for supporting and organizing cables. Cable trays can vary in design and are used for different applications.
When to use wire mesh cable tray?
Ventilation is Critical: The open mesh design allows for maximum airflow, reducing the risk of overheating.
Ease of Access is Required: They provide easy access to cables for installation, maintenance, or modifications.
Flexibility is Needed: They can be easily modified or expanded to accommodate changing cable needs.
What is the difference between a perforated cable tray and a channel cable tray?
Channel Cable Tray: Has a narrower, U-shaped profile and is typically used for smaller cable runs. It provides a more contained and compact path for cables compared to perforated trays.
Thank you for your interest in our products. To receive our pricelist or for any inquiries, please fill out the form below. We will get back to you within 24 hours.
