- Home
- Cable Tray Fittings
Cable Tray Fittings and Accessories Systems
Cable trays are essential components in electrical wiring for structures, supporting insulated electric cables used in industrial and commercial settings. Common types of cable trays include solid-bottom trays, cable channel or trough trays, ventilated trays, and ladder trays. Each type, including FRP cable tray, has specific cable tray fittings designed to maintain and support the cable tray system.Cable tray fittings connect various sections of trays, change the direction of runs, and accommodate different cable sizes and types. To withstand rigorous use and harsh environments, these fittings are often made from materials like hot-dipped galvanized steel, fiberglass, and aluminum. For enhanced mechanical and electrical connections, fittings may use a swaging process to attach rungs to the side members.
GangLong Fiberglass offers a wide range of cable trays and fittings, ensuring that you find the right components for your specific needs. Cable Tray Fittings systems – compatible with conduit, raceway & strut. Trusted distributor with engineering support.
Simplifying Your Life: Key Functionalities
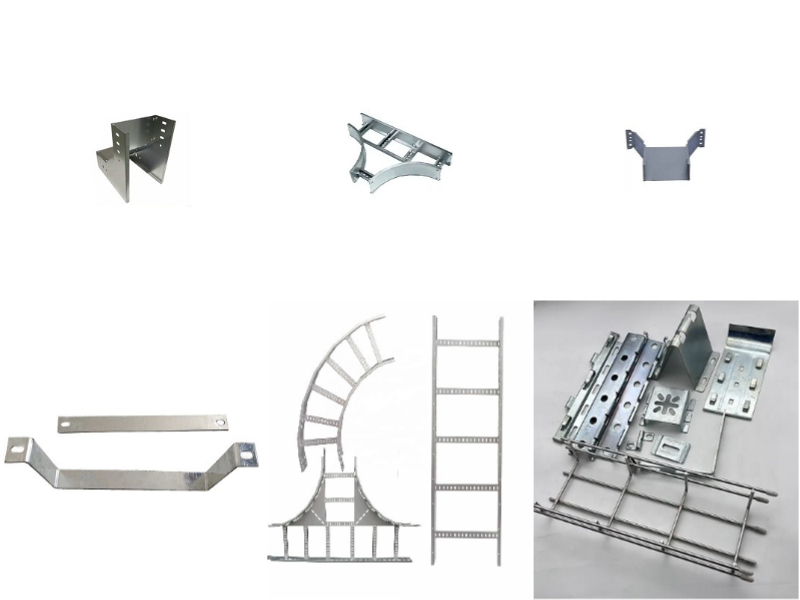
| Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Place of Origin | Hebei, China |
| Brand Name | GangLong Fiberglass |
| Product Name | Cable Tray Fittings |
| Material | Steel, Aluminum, Stainless Steel 304/316, Fiberglass |
| Finish | HDG, Powder Coating, E-plating |
| Width | Customized |
| Length | Customized |
| Thickness | Customized |
| Size | Customized |
| Side Rail Height | Customized |
| Color | Customized |
| Maximum Working Load | According to Size |
| OEM | Available |
| Certification | NEMA, CE, UL, IOS |
| Application | Power Cord and IT Cable Management |
| Sales Unit | Single Item |
| Supply Capacity | 4000 Meters per Day |
News
- Exploring the Benefits of Carbon Fiber Apparel
- How to Work with Carbon Fiber Successfully
- Carbon Fiber Suit: The Future of Lightweight Armor
- Is Carbon Fiber Armor the Future of Protection?
- Why White Carbon Fiber is Popular in Automotive Design
- Transparent Carbon Fiber Sheets Two Sided Gloss Twill
- Epoxy-Compatible Chopped Carbon Fiber Mat
- Carbon Fiber EG Hatch: Upgrade Your Civic Today
- The Benefits of Using Structural Carbon Fibre in Engineering
- How Many Layers of Layered Carbon Fiber Are Needed?
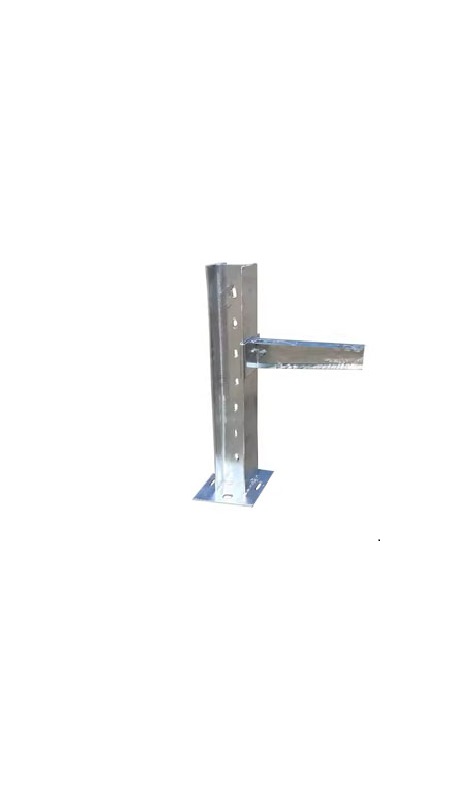

What Are Cable Tray Fittings?
Cable Tray Fittings are essential components used in cable management systems to facilitate the routing, protection, and organization of electrical cables. These fittings are designed to connect, route, and secure cables within cable tray systems, helping to ensure safety, reduce strain on cables, and maintain efficient cable routing. Cable tray fittings are crucial for creating flexible and scalable cable management solutions, whether for industrial, commercial, or residential applications. They enable the efficient passage of multiple cables, allowing for proper air circulation and reducing the risk of overheating or physical damage to cables.
These fittings come in various types, each serving a specific function within the system. From corner transitions to size adjustments, they ensure that the cable tray system can adapt to complex layouts while maintaining a secure and organized structure.
Choosing the Right Type of Cable Tray Fittings
Selecting the right cable tray fittings is essential for maintaining a safe, efficient, and future-proof cable management system. These components connect, branch, and support cable trays across a variety of environments — so making informed choices is crucial. Below are the key factors to consider during the selection process:
Application Requirements
Start by assessing the type of cable being routed — whether it’s power, communication, control, or multi-core. Determine the routing direction: do you need vertical drops, 90° turns, T-junctions, or reducers for size changes? Each scenario calls for specific fitting types, such as elbows, crosses, or reducers. Choosing the right configuration ensures smooth cable flow, organized layout, and minimal mechanical stress on cables.
Cable tray systems come in various materials, including galvanized steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and FRP (fiber-reinforced plastic). For structural integrity and uniform load-bearing properties, the fittings should match or be compatible with the tray material. For example, aluminum trays pair best with aluminum fittings to avoid galvanic corrosion, while FRP fittings suit chemically aggressive or outdoor environments. Environmental conditions significantly influence the longevity and performance of cable tray fittings. In dry indoor areas, standard steel or aluminum fittings may suffice. However, in outdoor, marine, or chemical plant settings, corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or FRP are preferred. Consider resistance to moisture, temperature extremes, UV exposure, and chemical agents when selecting materials and coatings. The physical dimensions and weight of the cables determine the size and structural strength required from your fittings. Heavy-duty cables, such as thick power lines or bundled control cables, demand reinforced or oversized fittings to prevent sagging, displacement, or long-term stress failure. Properly sized fittings not only protect cables but also maintain the system’s mechanical integrity. Efficient installation saves time and reduces labor costs. Look for fittings with features like slotted holes, snap-on covers, or pre-punched mounting points. These allow for quick alignment and adjustment on site. In maintenance-heavy environments, consider fittings with hinged or removable sections that enable fast access for inspections, cable additions, or replacements — without dismantling the entire tray.Tray Material Compatibility
Environmental Considerations
Load and Cable Size
Ease of Installation and Maintenance
Cable Tray Fittings Catalogue
Why the Cable Tray Fittings Catalogue Exists
The Cable Tray Fittings Catalogue is a practical, all-in-one reference for engineers, contractors, and system designers involved in cable management. It streamlines the selection and sourcing process by providing a detailed, organized overview of available fittings — including types, sizes, materials, and specifications. With clear compatibility guidance and technical data like load ratings and installation instructions, the catalogue simplifies decision-making, saves time during procurement, and ensures precise, project-ready solutions.
Benefits of Using the Cable Tray Fittings Catalogue
Streamlined Decision-Making
The catalogue consolidates a wide range of fitting options into a single, easy-to-navigate resource, enabling users to quickly find and compare products. This centralization eliminates the need to browse through multiple suppliers or datasheets, significantly simplifying the selection process and speeding up decision-making for engineers, procurement teams, and project planners.
Compatibility and Accuracy
Each product entry in the catalogue includes detailed specifications, dimensions, and system compatibility notes. This ensures that users select fittings that align precisely with their existing cable tray systems, reducing the risk of mismatches, installation errors, or performance issues. With accurate information at hand, users can proceed with confidence and avoid costly adjustments during installation.
From planning to procurement to installation, the catalogue supports efficiency at every stage. Users can quickly identify material options—such as galvanized steel, stainless steel, aluminum, or FRP—and review technical data like load capacities and environmental ratings. This clarity allows for smarter design decisions, faster product sourcing, and smoother execution on site. The catalogue offers a full spectrum of cable tray fittings, including elbows, tees, reducers, connectors, splice plates, and end caps. Whether the need is for directional changes, size transitions, or system terminations, every fitting type is clearly categorized and presented. This ensures that professionals can find exactly what they need—no matter how complex or customized the project. Choosing the right fittings requires more than checking part numbers. The catalogue provides detailed information on material types, sizing, load ratings, and environmental conditions. By reviewing each of these features, you can ensure a safe, efficient, and cost-effective cable tray system tailored to your project’s demands. Materials determine durability and application scope. Steel is ideal for strength and heavy loads. Aluminum resists rust and is easy to install. FRP excels in wet, chemical, or coastal environments. Selecting the correct material extends service life, lowers maintenance, and prevents premature failure under specific environmental and structural conditions. Match material to location for optimal performance. Accurate sizing is essential. The catalogue provides fitting dimensions like width, height, angle, and radius. Matching these to your tray system avoids strain, misalignment, and unsupported loads. A proper fit also improves installation speed and structural stability. Be sure to verify measurements before ordering to avoid costly installation errors or post-installation modifications. Each fitting must align with the tray type—ladder, perforated, wire mesh, or solid-bottom. The catalogue highlights system compatibility to ensure stable, secure connections. Some fittings also accommodate specific cable types like power or fiber. Confirming compatibility avoids installation delays, minimizes hardware conflicts, and ensures the tray system performs as designed under expected loads. Load ratings indicate how much weight a fitting can support without deformation or failure. These figures are essential for maintaining safety and system stability. Check ratings based on total cable weight, span, and tray configuration. Using under-rated fittings can lead to sagging, system failure, or downtime. Always choose fittings designed for your cable load. Fittings must withstand environmental challenges. Stainless steel resists corrosion, FRP handles chemicals, and UV-resistant materials work outdoors. Extreme heat, cold, moisture, and pollutants affect performance. The catalogue outlines each material’s resistance profile. Select fittings based on site conditions to reduce failure risk, extend service life, and maintain system integrity in demanding installations. Good catalogues include installation details: tools required, step-by-step instructions, safety precautions, and component compatibility. Some fittings have pre-drilled holes or quick-fit mechanisms to reduce labor time. Following the correct procedures ensures reliability, avoids damage, and speeds up deployment. Always review the instructions before installation to guarantee smooth assembly and proper system function. Eco-friendly products are increasingly important. Many fittings are recyclable or manufactured using sustainable processes. The catalogue may indicate compliance with LEED, RoHS, or ISO 14001. Choosing sustainable materials reduces waste and supports green initiatives. Consider long-term impact when selecting products, especially for government, commercial, or infrastructure projects requiring environmental responsibility. Not all systems use standard parts. The catalogue may offer custom options for non-standard tray sizes, angles, or finishes. Custom fittings reduce on-site adjustments and improve overall fit and performance. If your layout is complex or space-limited, customized components ensure a perfect match without sacrificing strength, safety, or system longevity.Efficiency Across the Project Lifecycle
Comprehensive Product Overview
Key Features to Consider When Reviewing the Cable Tray Fittings Catalogue
Material and Corrosion Resistance
Size and Dimensional Accuracy
Compatibility with Tray Types and Systems
Load Ratings and Support Capacity
Environmental Resistance
Installation Instructions and Requirements
Environmental Sustainability and Recyclability
Customization Options

Thank you for your interest in our products. To receive our pricelist or for any inquiries, please fill out the form below. We will get back to you within 24 hours.

Common Cable Tray Accessories List
Cable tray systems are often equipped with various accessories designed to improve their functionality, stability, and durability. These accessories are integral to the proper operation of cable trays, ensuring that cables are routed securely and efficiently while maintaining system integrity.
Common Cable Tray Accessories And Their Functions
Supports and Hangers
- Description: Supports and hangers are essential for mounting and securing cable trays to walls, ceilings, or beams when you build cable trays. They are designed to maintain the proper alignment and prevent sagging or shifting of the trays, ensuring a stable and efficient cable management system. These components are crucial for supporting classic cable tray installations, as they help distribute the weight of the cables evenly and resist vibrations that could potentially disrupt the tray’s structure. Properly installed supports and hangers ensure that the system remains secure and aligned, providing long-term performance and durability.
- Types:
- Wall Brackets: Used to attach trays to vertical surfaces.
- Ceiling Hangers: Suspended from ceilings to hold trays in place.
- Beam Clamps: Fixed onto beams to support horizontal cable trays.
- Benefits: These components provide the necessary stability to bear the weight of cables, ensuring the cable tray remains securely fastened and resistant to vibrations or mechanical stress.
Cable Covers
- Description: Cable covers protect cables from environmental hazards such as dust, moisture, and physical damage. They are typically placed over the open sections of the tray, shielding cables from external factors.
- Materials: Cable covers come in various materials, including:
- Metal (Steel, Aluminum): Provides durable protection against impacts.
- Plastic (PVC, ABS): Offers lightweight protection and is resistant to moisture and chemicals.
- Benefits: Cable covers help maintain the integrity and performance of cables by protecting them from contaminants, UV degradation, and physical damage.
Cable Straps and Ties
- Description: These accessories are used to bundle and secure cables within the tray. Cable ties and straps ensure that cables are neatly organized and remain in place throughout the installation and use of the tray.
- Materials: Common materials for cable straps include:
- Nylon: Flexible, adjustable, and suitable for indoor use.
- Stainless Steel: Ideal for high-temperature or harsh environments.
- Benefits: Cable ties and straps prevent cables from tangling, improve airflow, and reduce the risk of overheating. They also make maintenance easier by keeping cables easily accessible.
Elbows and Bends
- Description: Elbows and bends are used to change the direction of cable trays, facilitating routing around corners, obstacles, or tight spaces.
- Angles: These fittings are available in various angles, such as 45°, 90°, and adjustable bends, depending on the installation requirements.
- Benefits: Properly sized and installed elbows and bends ensure smooth transitions and prevent sharp bends in cables, which can cause signal loss or cable damage.
Tees and Crosses
- Description: Tee and cross fittings are used to branch out the cable tray system in different directions, allowing for multiple pathways to be created from a central point.
- Benefits: These fittings enable flexible routing and efficient use of space, especially in larger facilities or complex installations. They are critical in applications where cables need to be routed to multiple areas simultaneously.
Reducers
- Description: Reducers are used to transition between different-sized cable trays, ensuring smooth transitions between trays of varying widths.
- Benefits: They help create a seamless connection between trays of different sizes, accommodating varying cable types and volumes. Reducers are particularly useful in installations where cables need to be routed from a larger tray to a smaller one, or vice versa.
End Caps
- Description: End caps are used to close the open ends of cable trays, preventing cables from slipping out and protecting the tray from dirt, debris, and physical damage.
- Benefits: End caps provide safety by ensuring that cables stay secure within the tray while protecting them from external elements. They also improve the overall aesthetics of the cable tray installation by providing a clean, finished look.
Splice Plates
- Description: Splice plates are used to connect two pieces of cable tray, allowing for continuous cable routing.
- Benefits: Splice plates ensure that cable trays are securely joined, maintaining the structural integrity of the system. They are essential in larger installations where long stretches of cable trays need to be connected.
How Accessories Enhance Functionality in Cable Tray Systems
Cable tray accessories improve system performance by offering enhanced support, protection, organization, and routing flexibility. They’re essential for safe, efficient cable installations in both simple and complex environments. From securing cables to supporting expansion, these components ensure long-term reliability, safety, and professional presentation across industrial and commercial applications.
Stability and Support
Support accessories like wall brackets, hangers, and beam clamps keep cable trays aligned and firmly in place. They prevent tray sagging, shifting, and misalignment, which could lead to cable damage or failure. Even weight distribution across supports improves system durability, especially in areas exposed to vibration or structural movement that would otherwise compromise tray stability.
Protection Against Environmental Factors
Cable covers shield tray systems from dust, debris, chemicals, moisture, and impact. In harsh environments such as manufacturing plants, data centers, or outdoor locations, they help preserve cable integrity and performance. These covers are especially important in industries exposed to heat, corrosion, or mechanical stress where unprotected cables would quickly degrade or become hazardous.
Organization and Efficiency
Accessories like cable ties, clamps, and labels maintain a clean, organized tray layout. Bundled cables improve airflow, reduce heat buildup, and simplify maintenance or troubleshooting. Technicians can quickly identify circuits and make modifications safely. Proper organization also reduces tangling or accidental cable movement, which protects both cable function and the efficiency of the overall system.
Routing Flexibility
Routing accessories—such as elbows, tees, crosses, and reducers—allow the tray system to adapt to complex layouts. They enable smooth directional changes without sharp bends that could damage cables. These components support efficient use of space, maintain cable flow, and minimize mechanical strain. Their flexibility is crucial in installations with architectural constraints or limited clearance.
Safety and Aesthetics
End caps and splice covers close off sharp edges and exposed tray ends, reducing safety hazards and improving the system’s appearance. These accessories protect cables from dislodgement or accidental contact and offer a clean, finished look. In public or high-visibility spaces, a polished tray system conveys professionalism and aligns with modern safety standards.
Expansion and Modifications
Splice plates and joiners allow for fast, secure system extensions. As facilities grow, these accessories make it easy to add new tray sections without dismantling the existing system. They preserve structural integrity while enabling cost-effective reconfiguration. Their use ensures that your cable tray infrastructure stays adaptable to future layout or capacity changes.
Cable Tray Fittings Sizes
Cable tray fittings come in various sizes to cater to the diverse requirements of cable management systems, whether in residential, commercial, or industrial settings. Understanding the available sizes is essential to ensure that the fittings align with your cable tray system, providing a secure, functional, and efficient routing solution. Fittings must be carefully chosen to accommodate different cable types, volumes, and tray dimensions, as well as to meet the specific needs of the installation environment.
Common Sizes of Cable Tray Fittings
Standard Sizes
Most cable tray fittings are available in standard sizes that are designed to fit the most commonly used cable trays. These sizes typically follow industry standards and are widely available. Some of the most common standard sizes include:
- 2-inch Fittings: Ideal for smaller cable management systems, such as in residential buildings or smaller commercial spaces. These fittings are perfect for running lower volume or smaller cables like telephone lines or low-power electrical cables.
- 4-inch Fittings: A versatile size used in both residential and industrial applications. It is commonly used for low to medium-volume cable runs, including for electrical wiring, data cables, and some types of control wiring.
- 6-inch Fittings: These are commonly used in mid-sized commercial and industrial applications, such as office buildings or light industrial setups. They are capable of accommodating a higher volume of cables and are suited for larger electrical or communication networks.
- 12-inch Fittings: Typically used in heavy-duty industrial environments, such as manufacturing plants or large-scale commercial projects. These fittings can handle a larger volume of cables, including high-voltage power cables and thick data cables.
These sizes are available in a variety of fittings, including elbows, tees, reducers, and connectors, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of cable tray systems.
While standard sizes meet most cable management needs, some projects may require custom-sized fittings. Custom cable tray fittings are manufactured to fit specific project requirements, especially when dealing with non-standard tray sizes, unique configurations, or special angles. Custom sizes can accommodate: Selecting the correct size for cable tray fittings is a critical part of designing an efficient, reliable, and scalable cable management system. Fittings must be chosen not only to match tray dimensions but also to suit the cable type, installation environment, and future expansion needs. Below are the key factors to consider when determining the appropriate size for your application. Selecting fittings that match the cable tray’s width, height, and depth is essential for a secure and aligned installation. If dimensions are mismatched, it can lead to unstable connections, exposed cables, and safety hazards. Accurate measurement and checking manufacturer tolerances help ensure a proper fit and smooth system performance. The size of the fittings should accommodate both the type and volume of cables being routed. High-voltage or fiber optic cables often require larger fittings to prevent excessive bending or crowding. In contrast, control circuits and low-voltage lines can be routed through smaller fittings without compromising safety or efficiency. Different projects demand different fitting sizes depending on their scale and operational demands. Industrial setups typically require larger or custom fittings due to higher cable volumes and heavier loads, while residential or commercial installations may function effectively with standard-sized fittings designed for lighter cable systems. The function of the cable system directly influences the required fitting size. Power distribution networks demand larger fittings to support thick, high-voltage cables. Meanwhile, telecom, data, or fire alarm systems generally involve smaller cables, which can be efficiently routed through compact 2-inch or 4-inch fittings. Limited installation space or complex routing paths often require custom or space-saving fittings. In ceiling runs, wall cavities, or tight corners, standard fittings may not be suitable. Custom-sized elbows, narrow-angle tees, or low-profile connectors help maintain system integrity while adapting to spatial restrictions. Planning for future growth is a key part of sizing decisions. Oversized or modular fittings allow for additional cable runs without needing system overhauls. This foresight minimizes future costs and disruptions while ensuring your cable management system remains adaptable as requirements evolve.Custom Sizes
Choosing the Right Size
Cable Tray Dimensions
Cable Type and Volume
Project Requirements
Application Type
Space Constraints and Layout
Future Expansion


Applications of Cable Tray Fittings
Cable tray fittings are essential components in the installation and maintenance of cable tray systems, offering crucial support, flexibility, and functionality in managing electrical and communication cables across various industries. These fittings are designed to ensure a seamless, efficient, and organized cable management system that simplifies installation, maintenance, and future upgrades. Here’s a more detailed look at their application:
Key Functions of Cable Tray Fittings
Routing and Direction Change
One of the primary purposes of cable tray fittings is to enable smooth directional changes within a cable tray system. Components such as elbows, tees, and crosses allow trays to turn corners, split routes, or bypass structural obstacles without disrupting cable alignment. These fittings ensure that cables follow a controlled path, reducing the risk of excessive bending, tension, or mechanical stress that could compromise insulation or signal integrity. Proper routing fittings contribute to clean, efficient layouts that simplify future access and minimize cable damage over time.
Expansion and Modification
As infrastructure grows or changes, cable tray systems must be able to evolve alongside it. Fittings like splice connectors, reducers, and adapters allow for seamless expansion and reconfiguration. Whether you’re adding a new section of tray to accommodate more cables or transitioning between tray sizes, these fittings enable easy adaptation without needing to dismantle existing systems. Their modular nature helps future-proof installations, making it simple to scale up, re-route, or retrofit trays as electrical and communication needs evolve.
Safety and Protection
Safety is a top priority in cable management, and fittings contribute to that in multiple ways. End caps seal off open tray ends, preventing cables from slipping out or being exposed to accidental contact. Cable covers provide an additional layer of protection by shielding cables from dust, debris, UV light, or mechanical impact—particularly important in industrial or outdoor settings. These protective accessories help maintain system integrity and ensure compliance with safety standards, especially in environments where personnel or equipment may come into contact with the tray system.
Support and Alignment
No cable tray system can function properly without adequate support. Fittings such as wall brackets, ceiling hangers, and trapeze kits are used to anchor trays securely to structural elements like beams, ceilings, or walls. These supports maintain consistent tray alignment, preventing sagging, shifting, or misalignment over time. This is crucial not only for cable safety but also for maintaining system performance, especially in areas with vibration, high cable load, or long-span runs. Proper alignment also improves visual neatness and allows for easier cable access.
Ease of Maintenance and Upgrades
Cable tray fittings greatly simplify maintenance and system upgrades. Unlike conduit systems, which require pulling wires through enclosed pipes, tray systems allow open access to cables. This makes it easy to add, remove, or reposition cables as needed. Fittings help organize routes, define segments, and allow easy isolation of cable groups. As a result, technicians can perform upgrades or maintenance tasks quickly and with minimal disruption to ongoing operations—saving labor time and reducing costs over the system’s lifespan.
Application Aspects
Industries: Cable tray fittings are widely used across industries such as automotive, transportation, power generation, telecommunications, and data centers. In each of these sectors, reliable cable management is crucial to ensuring smooth, uninterrupted operations.
Harsh Environments: Since cable tray systems are often exposed to extreme weather conditions, such as rain, snow, and high winds, fittings are built to withstand harsh environments. For example, hot-dip galvanized steel, fiberglass, and aluminum fittings provide enhanced durability and resistance to corrosion and wear.
Regulatory Standards: Cable tray fittings must meet strict standards, including UL and NEMA VE-1 certifications, to ensure safety, performance, and compliance with electrical regulations. These standards guarantee that the fittings are properly designed and manufactured to handle the rigorous demands of electrical installations.
Cable tray fittings are indispensable for the efficient and secure routing, organization, and protection of electrical cables in a variety of settings. By enabling easy changes, offering structural support, and protecting cables from external damage, these fittings ensure the long-term functionality and safety of cable tray systems. Proper selection and installation of these fittings are key to achieving a reliable, durable cable management solution that meets the evolving needs of modern industries.
Purchase Custom Cable Tray Fittings
High-Quality Custom Cable Tray Fittings for Efficient Cable Management
For over a decade, we have specialized in cable tray systems, offering a wide range of custom cable tray fittings designed to support seamless cable management solutions. Our products are crafted from premium materials and manufactured with precision, ensuring durability, flexibility, and easy installation.
Why Choose Our Cable Tray Fittings?
Extensive Industry Experience
We’ve been designing and manufacturing cable tray fittings for over 10 years. This experience allows us to develop fittings that are not only high-quality but also practical for a wide range of installation environments. Our knowledge ensures that each product meets real-world demands in terms of durability, precision, and compatibility with various cable tray systems.
Versatile Options for Every Need
Our fittings come in a broad range of types and sizes, including elbows, tees, crosses, reducers, and more. No matter the shape or layout of your cable tray system, we provide compatible solutions. This versatility helps installers handle complex routes, height transitions, and directional changes quickly and securely.
Built with Premium Materials
We use galvanized steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, and FRP to meet diverse project needs. These materials are chosen for their strength, corrosion resistance, and longevity. Whether you need fire-resistant, rust-proof, or non-conductive solutions, we offer the right material for your application environment — from factories to outdoor plants.
Easy and Flexible Installation
Our cable tray fittings are designed for quick assembly and secure connections. The user-friendly design allows for fast adjustments and simplified cable routing on site. With pre-drilled holes and precision-fit components, our fittings help reduce installation time, minimize labor costs, and support flexible system upgrades when needed.
OEM/ODM Availability
We offer custom manufacturing for unique project requirements. From specific angles and sizes to material types and coatings, we can build fittings tailored to your application. Our engineering team works closely with clients to ensure each custom part meets technical standards, timelines, and budget — making your project fully optimized from the start.
Competitive Factory Pricing
We produce our fittings in-house, allowing us to manage quality and reduce extra costs. This means you get high-performance products at competitive prices. Our goal is to offer affordable solutions for both large-scale industrial jobs and smaller commercial installations, without compromising durability or compliance.
Comprehensive Selection of Cable Tray Fittings
As a leading cable tray manufacturer and supplier, we offer a full range of accessories and spare parts, including:
- Tray Brackets – Securely mount and support cable trays for optimal stability.
- Tray Connectors – Ensure seamless integration between tray sections.
- Support Systems – Customizable solutions for different load capacities and environments.
- Cover Clamps & Fasteners – Enhance tray protection and ensure secure installations.
Enhance Your Cable Management System with Reliable Accessories
Our custom cable tray fittings are engineered to meet industry standards while providing flexibility and durability for diverse applications. Whether you need standard components or custom-designed solutions, we are committed to delivering high-quality, cost-effective products tailored to your needs.
For inquiries or bulk orders, contact us today to explore our custom cable tray fitting solutions and get the best pricing for your project.
FAQs about Cable Tray Fittings and Cable Management
What are the five basic cable tray fittings?
Elbows: These fittings are used to change the direction of the cable tray, allowing cables to navigate around corners or bends. They come in various angles, such as 45 degrees or 90 degrees, depending on the direction needed.
Tees: Tees branch out from the main cable tray run, creating a junction where cables can be split off to another tray. This fitting is useful for directing cables to multiple locations from a central point.
Reducers: Reducers connect cable trays of different sizes, transitioning between larger and smaller trays. This fitting is crucial for adapting to changes in cable volume or tray dimensions.
Connectors: Connectors are used to join two sections of cable trays together, ensuring a continuous run. They provide a secure and stable connection, maintaining the integrity of the cable routing system.
End Caps: End caps are used to close off the ends of the cable trays. They prevent cables from falling out and protect the open ends from dust and debris.
What are the five basic cable trays fittings?
Elbows (90-degree and 45-degree): Used to change the direction of the cable tray horizontally or vertically.
Tee Fittings: Used to branch the cable tray into three directions.
Cross Fittings: Allow the cable tray to branch into four directions.
Reducers: Used to connect two cable trays of different widths.
Couplings: Used to join two sections of cable trays together.
What are the three main types of cable trays?
Ladder Cable Tray: Consists of two side rails connected by rungs. This is the most common type and is ideal for supporting cables over long spans.
Perforated Cable Tray: A solid bottom tray with small holes for ventilation. It provides excellent support and protection for cables while allowing for some air circulation.
Solid Bottom Cable Tray: A fully enclosed tray that provides maximum protection for cables, preventing dust, dirt, and moisture from entering. However, it lacks ventilation.
What is the standard for cable tray?
Are there cable fill requirements for cable trays?
NEC Article 392 specifies the maximum allowable cable fill in cable trays. The fill percentage varies depending on whether the cables are installed in a single layer or multiple layers.
NEMA VE 2 also provides guidance on cable tray fill, considering factors like cable type, size, and the need for adequate ventilation.
What are the electrical tools need in installing cable trays and wire ways?
Cable Cutters: For cutting cables to the desired length.
Fish Tape: For pulling wires through conduits or trays.
Drills and Drill Bits: For making holes in walls or supports.
Screwdrivers and Wrenches: For fastening trays, brackets, and fittings.
Level: To ensure the cable tray is installed evenly.
Tape Measure: For accurate measurements.
Cable Strippers: For removing insulation from the cables.
Pliers and Crimpers: For bending and connecting cables.
What are the accessories of cable tray?
Tray Covers: Protect the cables from dust, debris, and physical damage.
Cable Ties and Clamps: Secure the cables to the tray, preventing movement.
Splice Plates and Couplers: Join sections of cable trays together.
Support Brackets and Hangers: Secure the cable tray to walls, ceilings, or other structures.
Dropouts and Cable Retainers: Guide and secure cables as they exit the tray.
Cable Tray Dividers: Separate different types of cables within the same tray.
What is the difference between a perforated cable tray and a channel cable tray?
Channel Cable Tray: Is essentially a U-shaped tray with a solid or ventilated bottom. It is used for smaller cable runs and typically provides more protection than ladder or perforated trays but less ventilation.
What is the most commonly used type of wire in conduit and cable trays?
How many types of cable connectors are there?
Compression Connectors: Used to join or terminate cables, often requiring a crimping tool.
Set-screw Connectors: Use a screw to hold the cable in place, typically for conduit connections.
Push-in Connectors: Allow easy insertion of cables without the need for screws or crimping.
Couplings: Join two sections of cables or conduits.
Cable Glands: Provide strain relief and protect cables as they enter enclosures.
What is cable tray wire called?
What is the difference between cable tray and raceway?
Raceway: An enclosed conduit or duct that provides more protection to the cables from environmental factors. Raceways can be metal or plastic and are typically used where cable protection is critical.
What is the difference between a cable ladder and a cable tray?
Cable Tray: A broader term that includes various types like ladder trays, perforated trays, and solid-bottom trays. It supports cables and allows for routing and organization, with varying degrees of protection and ventilation depending on the type.
What are cable tray fittings?
Elbows (90-degree and 45-degree): Change the direction of the cable tray horizontally or vertically.
Tee Fittings: Allow for branching of cables in three directions.
Cross Fittings: Allow for branching in four directions.
Reducers: Connect two trays of different widths, typically when transitioning between different cable loads.
Splice Plates/Couplers: Join two sections of cable trays together.
End Caps: Seal off the end of a cable tray to protect cables and prevent entry of debris.
How to connect two cable trays?
Align the two cable tray sections end-to-end, ensuring that they are properly aligned.
Position the splice plates or couplers at the joint where the two sections meet.
Bolt or fasten the splice plates securely to both sections using the provided hardware. Ensure the connection is tight and that the trays are level and properly aligned.
Verify the joint for stability, ensuring there are no gaps or misalignments that could cause issues with cable support or movement.
What is the NEC code for cable tray support?
Cable trays must be supported at intervals not exceeding 1.5 meters (5 feet) for nonmetallic systems and 2.4 meters (8 feet) for metallic systems unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer.
Supports must be capable of withstanding the load of the tray, the cables within, and any additional environmental loads.
What are the advantages of cable tray fittings?
Flexibility in Installation: They allow for custom routing and changes in direction or elevation, making it easier to design complex cable systems.
Ease of Maintenance: Fittings facilitate easy access to cables for maintenance, upgrades, or re-routing without significant system disruption.
Improved Safety: By securely joining and guiding cables, fittings reduce the risk of damage, tangling, or stress on cables, enhancing overall system safety.
Scalability: Fittings make it easier to expand or modify the cable tray system as the needs of the installation change over time.
Why are cables tied down in cable tray?
Prevent Movement: To avoid displacement due to vibration, air movement, or other external factors.
Maintain Organization: Cable ties keep cables neatly bundled and separated, reducing clutter and making future maintenance easier.
Reduce Stress: Tying down cables helps distribute their weight evenly along the tray, preventing stress or sagging.
Enhance Safety: Secured cables are less likely to become a tripping hazard or to be accidentally damaged.
How do you pull a cable through a cable tray?
Plan the Route: Identify the path of the cable and ensure it’s clear of obstructions.
Use a Fish Tape or Pull Rope: Thread the fish tape or pull rope through the cable tray from the starting point to the endpoint.
Attach the Cable: Secure the cable to the fish tape or pull rope using a pulling grip or tape.
Pull the Cable: Carefully pull the fish tape or rope, guiding the cable through the tray. Have a team member feed the cable into the tray at the starting point to prevent twisting or kinking.
Secure the Cable: Once the cable is in place, tie it down at intervals to prevent movement.
Does cable tray need to be bonded?
How do l know what size cable tray l need?
Cable Quantity and Size: Calculate the total cross-sectional area of all the cables to be installed in the tray. The cable tray should accommodate this area while leaving extra space for future expansion.
Cable Type: Consider the type of cable and any applicable spacing requirements, especially for power cables, to prevent overheating.
Load Capacity: Ensure the tray can support the combined weight of the cables without sagging or structural compromise.
Environmental Factors: In environments with high dust, moisture, or other hazards, a larger tray may be necessary to accommodate additional protective measures like covers or separators.
How often should l support a cable tray?
Metallic Cable Trays: Generally, support should be provided every 1.5 to 3 meters (5 to 10 feet), depending on the manufacturer's specifications and the load of the cables.
Nonmetallic Cable Trays: Support is typically required every 1.2 to 1.8 meters (4 to 6 feet).
Heavy Loads or Long Spans: More frequent support may be necessary if the tray is carrying a heavy load or spans a long distance without additional structural support.
How are cable trays fixed?
Wall-mounted Brackets: Secure the tray to walls using brackets designed to hold the tray at the desired height.
Ceiling Hangers: Use threaded rods or other ceiling supports to suspend the tray from above.
Floor Supports: For trays close to the ground, use stands or posts to elevate the tray above the floor.
Clamp and Bolt Systems: Use clamps or bolts to secure the tray to the supports, ensuring it is stable and secure.
Expansion Joints: For long runs, include expansion joints to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction, preventing stress on the tray.
What is the spacing between cables in a cable tray?
Power Cables: Should be spaced to allow for heat dissipation and prevent overheating. A common guideline is to maintain at least a 1-inch (25 mm) separation between power cables.
Data and Signal Cables: These can typically be placed closer together, but it’s recommended to maintain a small gap to prevent physical damage and allow for easier identification and maintenance.
Mixed Cable Types: When installing power and data cables together, they should be segregated, either by physical barriers within the tray or by maintaining a larger separation distance.
What should be the distance between two cables when installing on one cable tray?
Minimum Distance: Generally, maintain a minimum distance of about 1 inch (25 mm) between power cables to allow for heat dissipation.
High-Voltage Cables: For high-voltage cables, larger separations might be necessary depending on the voltage level, typically following manufacturer recommendations or applicable codes like the NEC.
Data Cables: When installed with power cables, maintain a greater separation (e.g., 6 inches or more) to avoid electromagnetic interference (EMI). Using barriers or separate compartments within the tray can also help.
What is the minimum clearance between cable trays?
Horizontal Separation: Typically, maintain a minimum horizontal clearance of 12 inches (300 mm) between adjacent trays to allow for cable installation and maintenance.
Vertical Separation: For vertically stacked trays, a minimum clearance of 6 inches (150 mm) is recommended, but 12 inches (300 mm) is often preferred for easier access and better heat dissipation.
Obstructions and Walls: Ensure there’s enough clearance (often 2 inches or more) between the tray and any obstructions or walls to allow for proper air circulation and access for maintenance.
How should the cables be placed in the tray?
Organized by Type: Group similar types of cables together (e.g., power cables separate from data cables) to prevent interference and simplify maintenance.
Layering: Place the largest and heaviest cables at the bottom of the tray, with smaller, lighter cables layered on top.
Segregation: Use dividers or separate trays for different types of services, especially when dealing with power, control, and communication cables.
Securing Cables: Cables should be secured at intervals using cable ties or clamps to prevent movement and maintain organization within the tray.
How far can you span cable tray?
Steel and Aluminum Trays: Typically, these trays can span up to 10 feet (3 meters) between supports without significant sagging.
Fiberglass Trays: These may require more frequent support, usually spanning up to 6 feet (1.8 meters).
Heavy Loads: For trays carrying heavy cable loads, reduce the span distance to prevent sagging and structural stress, potentially reducing spans to 4 to 6 feet (1.2 to 1.8 meters).
What is the minimum distance between cables?
Power Cables: A minimum of 1 inch (25 mm) is generally recommended to allow for adequate ventilation and heat dissipation.
Data Cables: Can be placed closer together, but maintaining a small gap of about 0.5 inches (12 mm) can help with organization and prevent physical damage.
High-Voltage Cables: May require larger separations, following specific manufacturer or industry guidelines to prevent voltage drop or electrical interference.
Which cable should not be in the same tray?
Power and Communication Cables: These should be separated to avoid electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can affect data transmission quality.
High and Low-Voltage Cables: High-voltage cables should not be mixed with low-voltage control or signal cables to prevent electrical interference and potential safety hazards.
Fire Alarm Cables and Others: Fire alarm cables should be kept separate from other services to ensure their integrity in case of a fire, following local codes like the NEC or NFPA.
What is the spacing for cable tray rungs?
Standard Spacing: Rung spacing is usually set at 9 inches (225 mm) apart for most cable trays. This spacing provides adequate support for cables and prevents sagging.
Heavy Loads: If the tray will support heavier cables, closer rung spacing of 6 inches (150 mm) may be required.
Light Loads: For lighter cable loads, the rung spacing could be extended to 12 inches (300 mm), but this depends on the specific installation requirements.
Is it necessary to provide tie down cables installed in a cable tray?
Prevent Movement: Tying down cables prevents them from shifting or becoming disorganized, especially in environments with vibration or movement.
Improve Safety: Securing cables reduces the risk of damage, which could lead to shorts or failures, particularly in high-voltage applications.
Maintain Organization: Tie-downs keep cables organized, making it easier to identify and troubleshoot issues.
Compliance: Many electrical codes and standards require cables to be secured at regular intervals to ensure a safe and reliable installation.
How far apart should wires be?
Power Cables: Should be spaced at least 1 inch (25 mm) apart to allow for heat dissipation and to prevent overheating.
Data Cables: Can be placed closer together, but a small gap (e.g., 0.5 inches or 12 mm) can prevent tangling and physical damage.
Mixed Cable Types: When installing both power and data cables, maintain a greater separation distance (e.g., 6 inches or more) to minimize the risk of electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Electrical Code Requirements: Always refer to local electrical codes, such as the NEC, for specific spacing requirements, particularly in sensitive or high-risk installations.
Does tray cable need to be in conduit?
Why use cable tray instead of conduit?
Ease of Installation: Cable trays provide a more straightforward installation process, especially for large quantities of cables. Cables can be laid into the tray without needing to be pulled through conduit, which can be time-consuming.
Flexibility: Cable trays allow for easier changes or expansions. New cables can be added or existing cables removed without major modifications.
Better Airflow: Cable trays provide superior ventilation, which helps with heat dissipation, reducing the risk of overheating, especially in high-capacity installations.
Cost Efficiency: Cable trays can be more cost-effective than conduit for large installations because they require less material and labor.
Accessibility: Cables in trays are more accessible for maintenance, troubleshooting, or future upgrades.
Can tray cable be direct buried?
Are cable splices permitted in a cable tray?
Splicing Methods: The splices must be made using approved methods and materials, such as splice kits or junction boxes designed for the type of cable and environment.
Access: The splices must be accessible for inspection, maintenance, and repair, as per NEC Article 392.
Protection: The splice must be properly insulated, secured, and protected from physical damage.
Tray Type: In some cases, splices may need to be enclosed in a protective cover or installed in a section of the tray with additional shielding to ensure safety and integrity.
How often should cable tray be supported?
Material: Metallic cable trays typically need support at intervals of 8 to 10 feet (2.4 to 3 meters). Nonmetallic trays may require more frequent support, often every 4 to 6 feet (1.2 to 1.8 meters).
Load: Heavier cable loads may necessitate closer support intervals to prevent sagging and ensure structural integrity.
Span Recommendations: Manufacturer guidelines and local codes (such as NEC Article 392) provide specific recommendations on support spacing based on tray type and load capacity.
Environmental Conditions: In environments subject to vibrations or other dynamic forces, closer support spacing may be required to ensure stability.
Can you run cable without conduit?
Cable Tray Systems: Cables can be installed directly in cable trays without conduit, as long as the cables are rated for open-air installation and the tray provides sufficient mechanical protection.
Exposed Runs: Some cables, like Type TC-ER (Tray Cable – Exposed Run), are designed for installation without conduit even outside of cable trays, provided they are supported and protected from physical damage.
Residential and Commercial Wiring: In some residential and commercial settings, cables like NM (non-metallic sheathed) or AC (armored cable) can be run without conduit, following local electrical codes.
However, in areas where the cables are subject to physical damage or environmental hazards, conduit may be required for additional protection.
Shall cable tray runs be before conductors are installed?
Structural Installation: The cable tray is first securely mounted and supported according to the design plan, ensuring it is level, properly aligned, and adequately supported.
Inspection: Before installing cables, the tray system should be inspected to ensure all connections are secure, and there are no sharp edges or other hazards that could damage the cables.
Cable Placement: Once the tray system is in place, cables can be laid into the tray. This allows for more straightforward and organized cable installation, reducing the risk of damage or misalignment.
Final Securing: After the cables are placed, they should be secured within the tray using cable ties, clamps, or other appropriate methods to prevent movement.
This sequence ensures a safe, efficient, and organized installation, allowing for easier access during the cable pulling and installation process.
What is the NEC standard for cable tray installation?
What type of cable is not allowed to be installed on a cable tray?
What is 5 core cable?
Thank you for your interest in our products. To receive our pricelist or for any inquiries, please fill out the form below. We will get back to you within 24 hours.
